Energy Monitoring Solutions – Cost Savings and System Performance Optimization
Comprehensive and Effective Energy Monitoring Solution (EMS)
In the era of industrial modernization and operational optimization, Energy Monitoring System (EMS) has become an indispensable tool for efficient energy management. EMS not only helps save energy and reduce costs but also ensures safety and sustainability in production activities.
Importance of Energy Monitoring
The EMS is a comprehensive management tool that monitors, analyzes, and optimizes energy usage. With advancements in IoT and AI, EMS offers numerous benefits to businesses, enabling intelligent and efficient energy management.
| EMS Benefits | Details |
|---|---|
| Energy Savings | Minimize losses and optimize energy costs. |
| Improved Equipment Performance | Real-time device monitoring reduces downtime. |
| Safe and Stable Operation | Early warnings for potential risks or energy-related issues. |
| Environmental Protection | Reduce CO2 emissions, aligning with ISO 50001 and other environmental standards. |
| Enhanced Productivity | Maintain stable energy sources for continuous and efficient production. |
Integrating EMS with Key Industrial Sectors
EMS solutions are effectively applied across five critical areas of production operations, significantly enhancing efficiency and energy savings.
1. Boiler Systems
- Operating Model: Boilers consume significant energy, especially in heavy industries. Monitoring pressure, steam flow, and temperature ensures high efficiency.
- Monitoring Devices:
- Temperature Sensors: Proline TMT.
- Steam Flow Measurement: Prosonic Flow.
- Pressure Sensors: Cerabar.
- Features: Real-time steam consumption tracking, combustion efficiency analysis, and pressure limit alerts.

Operational Model and Monitoring Devices for Boiler Systems
| Description | Monitoring Devices |
|---|---|
| Feedwater |
– Prowirl: Measures feedwater flow. – RTD: Measures feedwater temperature. |
| Fuel Input (Heating) |
– Coriolis: Measures fuel flow. – Loadcell: Measures mass for biomass fuel like wood chips. – Inverter: Adjusts conveyor speed for biomass systems. |
| Steam Output |
– Prowirl: Measures steam flow. – Cerabar M: Measures steam pressure. |
Energy Calculation Features of RSG 45
- Collects input data such as:
- Feedwater quantity and temperature.
- Fuel flow rates.
- Collects output data such as:
- Steam volume and temperature/pressure.
Based on this data, RSG 45 provides critical information such as:
- Boiler efficiency.
- Fuel and steam consumption.
- Energy usage.
- Total energy losses.
This solution not only optimizes boiler operations but also ensures energy efficiency and reduces production costs.
2. Cooling Systems
- Operating Model: Maintains stable temperatures, requiring close monitoring to optimize energy consumption.
- Monitoring Devices:
- Temperature Measurement: iTHERM TrustSens.
- Flow Meter: Promass.
- Controller: RSG45.
- Features: Tracks cooling efficiency, auto-adjusts capacity based on load, minimizes energy waste.
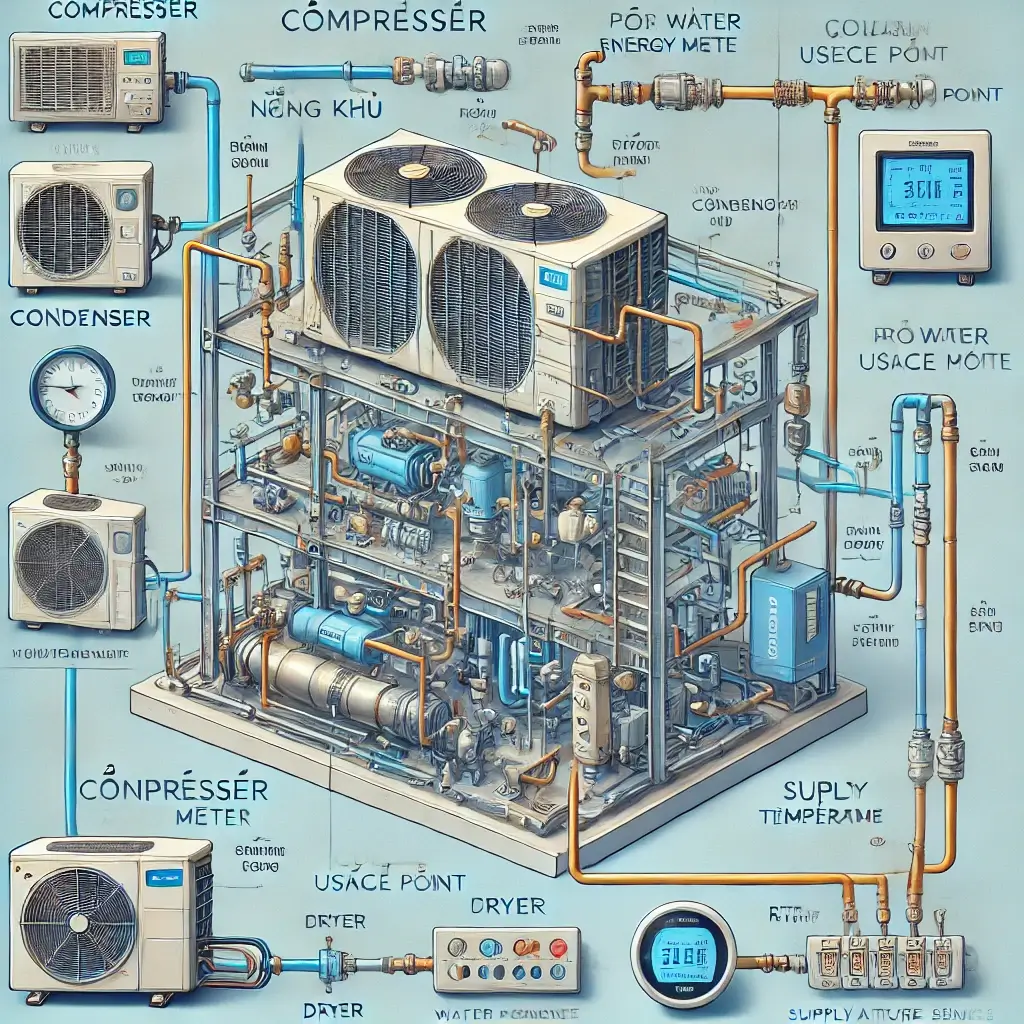
Operational Model and Monitoring Devices for Cooling Systems
| Description | Monitoring Devices |
|---|---|
| Compressors | – PM2230: Monitors compressor energy usage. |
| Condenser → Dryer |
– Prowirl: Measures water flow. – Cerabar M: Measures pressure. – RTD: Measures water temperature. |
| Dryer → Usage Points |
– PM2230: Monitors energy usage. – Prowirl: Measures water flow. – RTD: Measures input/output water temperatures. |
Energy Monitoring and Calculation Features of RSG 45
The RSG 45 collects data from cooling systems such as:
- Water flow, temperature, and pressure.
- Energy consumption of compressors and pumps.
Based on this data, RSG 45 provides:
- Cooling system efficiency (COP/COSP).
- Pump performance.
- Total energy consumption.
- Recovered heat losses.
- Cooling energy losses.
This system helps businesses monitor and optimize cooling efficiency, saving energy and reducing operating costs.

