How to Wire a NEMA 5-50 Receptacle (50A – 125V): The Definitive Technical & Safety Guide
If you are dealing with heavy-duty 120V equipment, correctly installing a NEMA 5-50R is critical. Unlike standard household outlets, a 50-amp installation leaves zero margin for error. A loose connection or wrong wire size can lead to catastrophic failure.
This guide provides a comprehensive technical breakdown of how to wire a NEMA 5-50 receptacle safely, complying with NEC standards.
⚡ Quick Summary: The Essentials
To safely wire a NEMA 5-50R, you must adhere to these core requirements:
- Wire Size: You must use #6 AWG Copper wire. (See our detailed guide on wire size for 50A breakers for the calculations behind this).
- Breaker: Connect to a 50A Single-Pole Circuit Breaker.
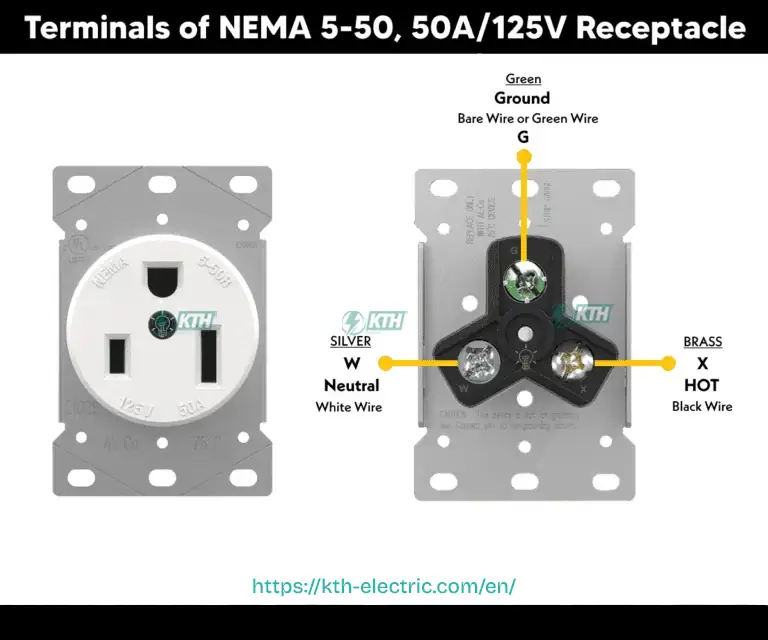
- Connections: Hot (Black) to Brass screw; Neutral (White) to Silver screw; Ground (Green/Bare) to Green Hex/U-shaped screw.
- Torque Spec: Standard torque for terminal screws is 30 lb-in (3.4 N·m).
1. Technical Specifications & Material Requirements (Critical Specs)
Before you strip a single wire, you must cross-reference your materials with mandatory specifications. This ensures fire safety and compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC).
If you are unsure about the terminology between different connection types, please refer to our comparison on Socket vs Outlet vs Receptacle.
| Specification | Technical Requirement | Important Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 125V AC, Single Phase, 60Hz | DO NOT connect to a 240V double-pole source. |
| Amperage | 50 Amps | Max continuous load: 40A (80% Rule). |
| Wire Configuration | 2-Pole, 3-Wire Grounding | Hot, Neutral, Ground. |
| Wire Size | #6 AWG Copper | Must comply with NEC Table 310.16. |
| Circuit Breaker | 50A, Single-Pole | Use GFCI if installed outdoors or in damp locations. |
| Electrical Box | 2-Gang Box | 50A receptacles are typically too bulky for 1-Gang boxes. |
| Torque | 30 lb-in (3.4 N·m) | Loose connections cause arcing and overheating. |
The NEMA 5-50R (125V) looks extremely similar to the NEMA 6-50R (240V) often used for welders.
Check your equipment carefully. If your device plate reads “240V” or “250V,” DO NOT follow this guide. This guide is strictly for 120V (125V) systems. Connecting a 120V device to 240V will destroy the equipment.
If you suspect your current electrical system has issues or was installed incorrectly, consider a professional Electrical System Assessment before proceeding.
2. Detailed Wiring Diagram
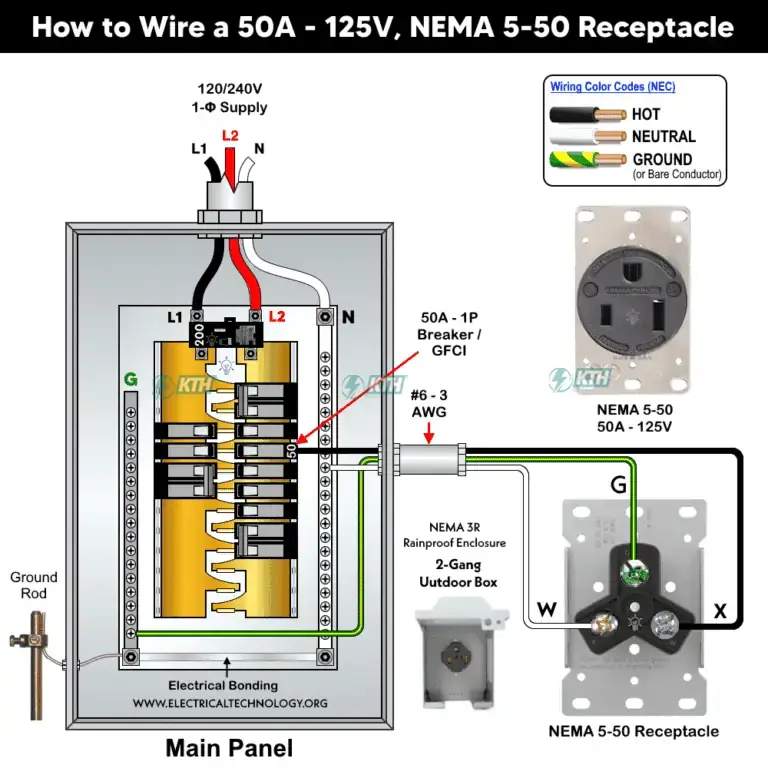
The circuit path involves three dedicated wires: Black (Hot) to the 50A Breaker, White (Neutral) to the Neutral Busbar, and Green/Bare (Ground) to the Ground Busbar.
The circuit path for a NEMA 5-50 consists of three distinct wires running from your main service panel to the receptacle. Understanding this path is crucial for proper Electrical System Maintenance.
Hot Wire (Black)
Runs from the load terminal of the 50A Single-Pole Breaker.
Neutral Wire (White)
Runs from the Neutral Busbar in the panel.
Ground Wire (Green/Bare)
Runs from the Ground Busbar in the panel.
3. Step-by-Step Installation Process
Follow this exact protocol to ensure a safe installation.
Safety & Preparation
Power Off: Turn OFF the main breaker or the specific branch circuit breaker. Verify power is off using a non-contact voltage tester.
Strip Wire: Strip approximately 1 inch (25mm) of insulation from the ends of the #6 AWG wires. Be careful not to nick or damage the copper strands.
Identify Receptacle Terminals
Examine the back of the NEMA 5-50R. Identifying the correct terminals is vital:
- Green Screw (U-Shaped): For the Ground wire.
- Silver Screw (Long Slot): For the Neutral (White) wire.
- Brass Screw (Short Slot): For the Hot (Black) wire.
Connect the Wires
Priority: Connect the Ground wire first to ensure safety during the process.
Insertion: Insert the stripped copper core fully into the appropriate terminal slot.
Torque: Using a screwdriver (preferably a torque screwdriver), tighten the screws to 30 lb-in.
Note: Ensure no stray copper strands stick out, as they could touch the metal box or other wires, causing a short circuit.
Install into the Wall Box
Carefully fold the #6 AWG wires (which are stiff) into the 2-Gang box.
Secure the receptacle to the box frame using the provided mounting screws.
Faceplate: Install the faceplate. Crucial: If installing outdoors, you MUST use a NEMA 3R weatherproof “In-Use” cover.
Termination at the Main Panel
Connect the Ground wire to the Ground Bar.
Connect the Neutral wire to the Neutral Bar.
Connect the Hot (Black) wire to the terminal screw of the 50A Single-Pole Breaker.
Testing: Turn the breaker ON. Use a multimeter (similar to how you might test a capacitor) to verify voltage:
- Hot to Neutral: ~120V (±5%)
- Hot to Ground: ~120V
- Neutral to Ground: 0V
4. NEC Codes & Safety Regulations
Installations must comply with NEC 210.8 (GFCI for wet locations) and NEC 210.19(A)(1) (80% load rule for continuous use).
Professional electricians always adhere to the code. Ensure your installation complies with the National Electrical Code (NEC):
NEC 210.8 (GFCI Protection)
If this receptacle is installed in a garage, unfinished basement, outdoors, or wet location, you are REQUIRED to use a 50A Single-Pole GFCI Breaker.
NEC 210.19(A)(1) (The 80% Rule)
While the receptacle is rated for 50A, if the load runs continuously for 3 hours or more (continuous load), the maximum current is limited to 40A (50A × 0.8).
For deeper understanding of load curves, refer to our article on Overload Relays and Trip Curves.
Power Capacity Calculations:
- Instantaneous Load: 120V × 50A = 6,000 Watts.
- Continuous Load: 120V × 40A = 4,800 Watts.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are the most common questions we receive regarding high-amperage installations.

