What is the Suitable Wire Size for 50A Breaker and Outlet? (NEC Guide)
Part 1: The Golden Rule of Wire Sizing
How to Determine the Correct Wire Size for a 50A Breaker and Load Circuits Based on NEC?
💡 Quick Answer: The correct wire size for a 50A circuit is typically #6 AWG Copper or #4 AWG Aluminum.
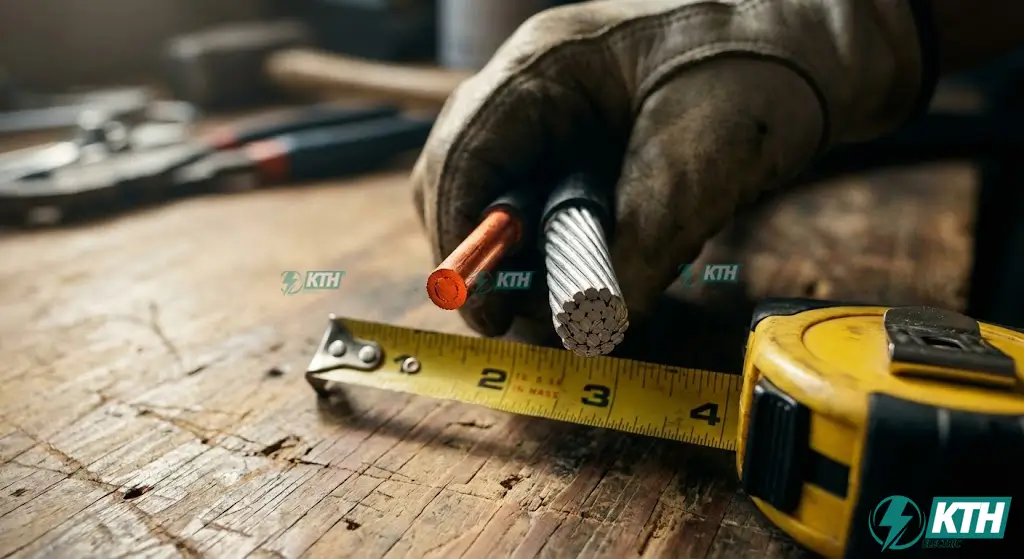

50-Amp breakers and outlets are heavy-duty circuits used for high-power equipment such as hot tubs, spas, EV charging stations, campers and RVs, air conditioner condensers, electric stoves, ranges, cooktops, water heaters, and other HVAC applications. 50A standard size outlets and breakers are available in both 1-pole and 2-pole configurations, used in 120V, 240V, and other voltage systems.
In this technical guide, we demonstrate how to determine the correct wire size for a 50A breaker and load circuit in AWG for personal and circuit protection in compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) NFPA 70. Before upgrading any heavy-duty system, we always recommend a professional electrical system assessment to ensure your infrastructure can handle the load.
What is the Right Wire Size for a 50A Breaker and Outlet?
💡 Standard Requirement: According to NEC Table 310.16, use #6 AWG Copper. If using Aluminum, use #4 AWG due to its lower conductivity.
The standard wire size for a 50-ampere breaker is #6 AWG copper wire according to the NEC Table 310.16. Alternatively, you need to use a #4 AWG aluminum wire with a 50-amp circuit because aluminum has higher resistance and lower conductivity compared to copper.
Both #6 AWG copper and #4 AWG aluminum wires can safely handle:
- 55A at 60°C (140°F)
- 65A at 75°C (167°F)
- 75A at 90°C (194°F)
Due to the heavy-duty nature of the circuit, you should use #6 gauge solid copper wire instead of #4 gauge aluminum or stranded wire with 50A breakers, outlets, and load circuits to ensure safety, better conductivity, and overall efficiency. Solid wire has several advantages over stranded wire, which is why U.S. homes typically use solid wire.
Key Rules to Remember:
- For a 50A circuit breaker, the correct wire size is #6 AWG for copper and #4 AWG for aluminum.
- A 50A breaker is used for a single appliance as a dedicated circuit for high-power devices. Similarly, a 50-amp outlet should be used for a single device.
- 120V Circuits: Use 14-2 with ground.
- 240V Circuits: Use 14-3 with ground (or 14-4 with neutral and ground for outlets like NEMA 14-50R).
- Longer runs: When the distance is more than 50 ft (15.25 meters), upgrade to a larger wire gauge to compensate for voltage drop. According to NEC 310-16, add 20% of additional ampacity for every 100 feet (30.50 meters) to counter the voltage drop.
Part 2: Load Calculations & Breaker Selection
How to Select the Right Wire Size for a 50A Breaker and Outlet?
Correct selection depends on whether the load is continuous or non-continuous. For engineers preparing for technical roles, understanding these calculation rules is often part of electrical engineering interview questions.
Example Scenario:
Determine the correct wire size for a 50-Amp (either 1-pole or 2-pole) breaker and outlets used for both continuous and non-continuous load circuits according to NEC guidelines.
1. Continuous Load Circuit
The NEC’s 125% rule states that the maximum overcurrent protection (MOCP) should handle 125% of the continuous load. As a safety factor, no more than 80% of the continuous load should be connected to the Overcurrent Protection Device (OCPD).
Calculation: $50A \times 80\% = 40A$
Based on this rule, the amperes of the load circuit should not exceed the maximum limit of 40A. Alternatively, you may only wire a 40-Amp continuous load (which lasts for 3-4 hours simultaneously, such as water heaters) to a 50-Amp breaker. If a device’s nameplate shows a Minimum Circuit Ampacity (MCA) of 40A:
$40A \times 125\% = 50A$
According to NEC Table 310.16, the #6 AWG copper wire size can carry 55A at 60°C and 65A at 75°C, which falls perfectly in the range of a 50A breaker.
2. Non-continuous Load Circuit
For non-continuous loads (e.g., general lighting circuits), the conductor size should be no less than 100% of the load. This way, a 50A breaker can handle a maximum of 50A non-continuous load circuits, while considering distance and ambient temperature rating (Refer to 110.14(C) and 310.15(B)(2)).
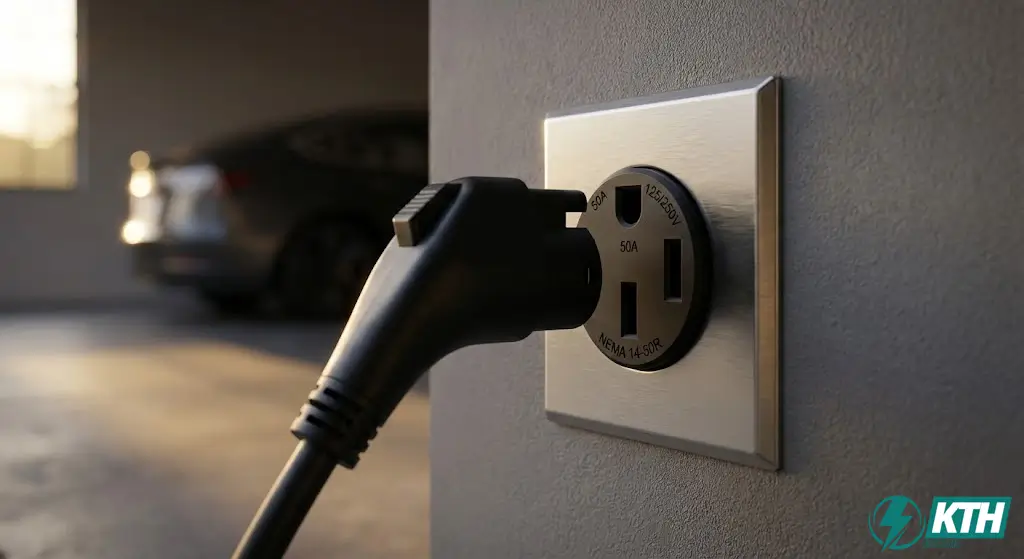

How Many Amps Can a 50A Breaker and Outlet Handle Safely?
💡 Safety Limit: A 50A breaker handles a maximum of 50A. However, for continuous loads (3+ hours), limit it to 40A (80% rule).
A 50-amp breaker safely handles a maximum of 50 amps of current. However, for continuous loads, you should not load breakers to more than 80% of their capacity.
- Continuous Load: Use a 50A breaker for a 40A max load.
- Non-continuous Load: Use a 50A breaker for a 50A max load.
These ratings comply with NEC Sections 210.19(A), 215.2, and 230.42(A).
Part 3: Power Capacity & Compatibility
How Many Watts Can a 50A Breaker and Outlet Hold?
💡 Power Limit:
120V Circuit: Max 6,000 Watts (Safe: 4,800W).240V Circuit: Max 12,000 Watts (Safe: 9,600W).
You can calculate the power capacity using the standard power formula.
1. 120V Circuit
In a standard 1-Pole, 120V circuit, the max power a 50A breaker can hold is:
$50A \times 120V = 6,000W$
Safe Continuous Load (80%): $40A \times 120V = 4,800W$
This allows using a 50A breaker with NEMA-5-50R outlets for devices like 4.5kW to 4.8kW electric water heater elements.
2. 240V Circuit
A 2-Pole, 50A breaker in a 240V circuit can hold:
$50A \times 240V = 12,000W$
Safe Continuous Load (80%): $40A \times 240V = 9,600W$
This allows you to use a 50A breaker with 240V, 9kW to 9.5kW electric ranges.
Is it Allowed to Use a 40A Outlet on a 50A Breaker?
🚨 Safety Alert:
NO. According to NEC, you can use a 50A outlet on a 40A breaker, but never put a 40A outlet on a 50A breaker.
No. According to NEC, it is allowed to use a 50A outlet on a 40A breaker, but never the reverse.
- NEC Compliance: NEC Article 210.21(B)(3) requires the outlet rating to be equal to or greater than the breaker rating. A 40A outlet on a 50A breaker violates this.
- Fire Risk: A 50A breaker will not trip at 45A, but a 40A outlet may overheat at that load, creating a fire hazard. To detect such overheating issues early, we recommend a thermal scan electrical cabinet service.
How Many Outlets Can be Put on a 50A Breaker?
50A breakers are generally used for a dedicated circuit for high-wattage appliances. It is against the code to wire multiple standard outlets to it. While mathematically you could calculate ($40A \div 1.5A \approx 26$ outlets), 50A breakers are practically hardwired for one device per outlet to ensure safety.
Part 4: Cable Types & Applications
What are the Suitable Types of Cables?
When selecting cables, ensuring the insulation integrity is as critical as the conductor size. For advanced monitoring, check our insulation monitoring solutions.
- Copper Conductors: 6 AWG Copper Wire is typical. Insulation types like THHN (Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated) or THWN are commonly used due to their durability.
- Aluminum Conductors: 4 AWG Aluminum Wire is required because aluminum is less conductive. Use THHN or XHHW insulation.
Applications of 50-Amp Breakers and Outlets
- RVs (Recreational Vehicles): Standard for RV parks to power air conditioners and refrigerators.
- Electric Ranges & Water Heaters: Required for high power demands.
- Hot Tubs & Spas: To handle heaters and pumps safely.
- EV Chargers: Level 2 EV chargers often require a 50A circuit.
- Subpanels: Often used to feed a subpanel in a garage or workshop.
Good to Know:
- For inductive loads (motors and HVAC), refer to NEC Article 440. If dealing with specific motor machinery, you might also be interested in our guide on DC Machines.
- Always ensure the ampere rating of a single receptacle does not exceed the branch circuit rating.
- Drawing more than 40A simultaneously from a 50A breaker continuously will overheat the circuit.
For those looking to deepen their knowledge on electrical standards, we highly recommend reading the Top 7 Essential Books for Electricians 2025. Additionally, for practical troubleshooting, learn how to test a capacitor correctly. If you need professional assistance, feel free to contact us.

